Don't miss the chance to work with top 1% of developers.
Sign Up Now and Get FREE CTO-level Consultation.
Confused about your business model?
Request a FREE Business Plan.
How Much Does Smart Contract Development Cost? Pros, Cons, and More
Table of contents

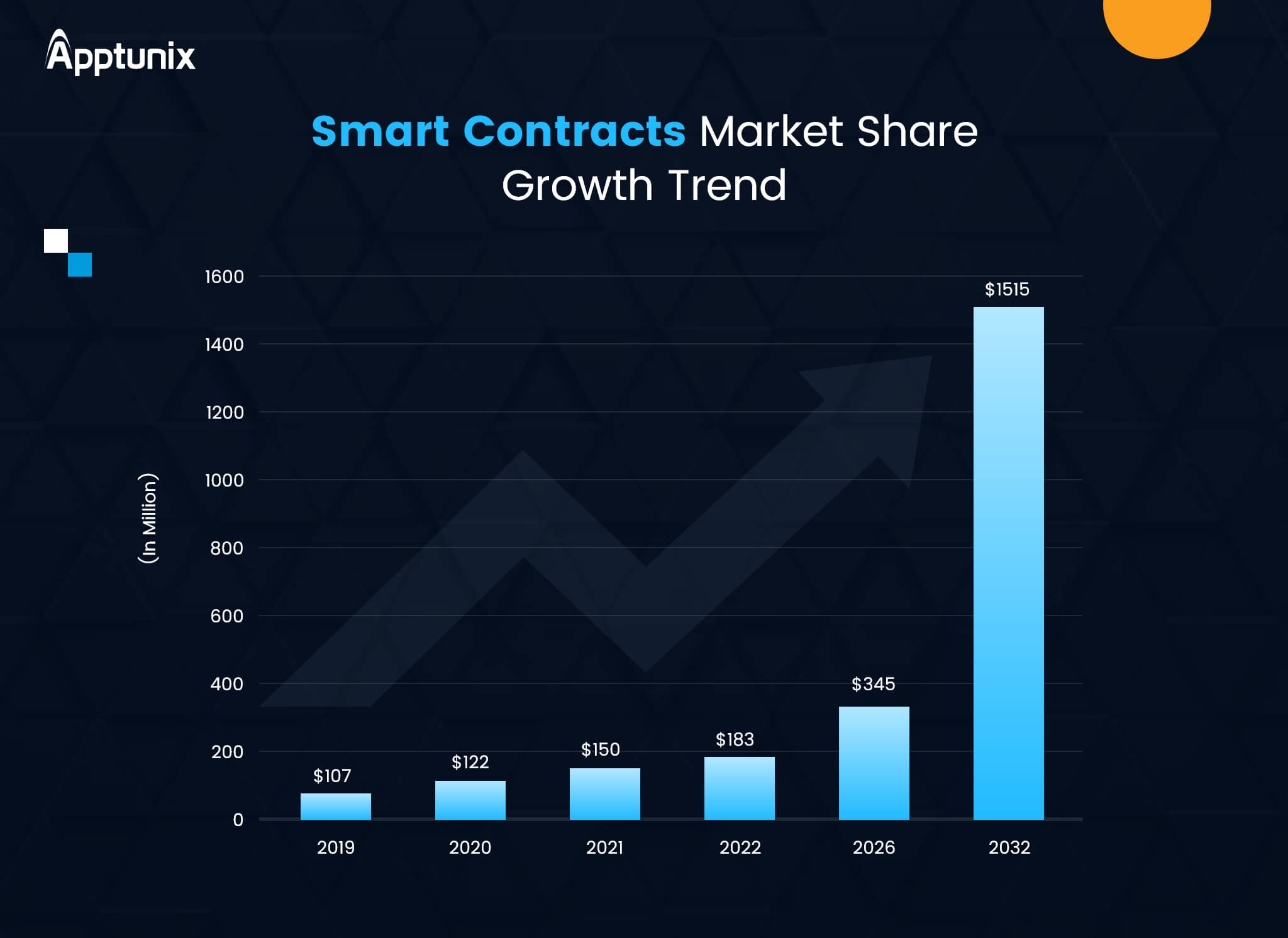
When smart contracts were first reintroduced by Ethereum back in 2015, people were skeptical about their importance. Fast forward to 2023 and businesses across the globe are vying for smart contract development. In 2022, the smart contracts market was valued at $183 million and is expected to cross $1.5 billion by 2032.
Reintroduced, yes, you read that right! Ethereum wasn’t the one who birthed the concept of smart contracts. It was the one who bolstered the idea though. In fact, it was Nick Szabo – the pioneer of blockchain and the possible contender for Satoshi Nakamoto – who coined the term during the early 90s.
Smart contracts make it possible to remove intermediaries from financial transactions. This not only brings down the cost but also makes the process more efficient, faster, and less prone to conflicts.
Interestingly enough, a vending machine can serve as a typical example of the implementation of smart contracts. If you’re looking to leverage smart contract development for yourself and want to know the estimated development cost, then you’re in the right place.
While we already talked about How to Get Started with Blockchain App Development in our last guide, in this blog post, we will discuss more about smart contracts. How smart contracts benefit your business, how much it costs to develop a smart contract, and the shortcomings of smart contracts – let’s discuss it all!
What are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a program on a blockchain that comes into action once certain conditions are met. It is a self-executing contract that is programmed in such a way that a certain action is carried out when some specific conditions are met successfully.
In simple terms, smart contracts let two or more people or businesses exchange something of a certain value in a transparent and conflict-free ecosystem without the need for any third-party like a banking institution or a real estate broker.
A smart contract is executed on the blockchain. This means that the terms are stored on a distributed database that doesn’t allow changing them.
Smart contracts serve a fundamental purpose in the implementation of DeFi (decentralized finance) applications. They are also among the top applications of blockchain, other than NFTs, and cryptos.
Also Read: What is DeFi Lending and How Does it Work?
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
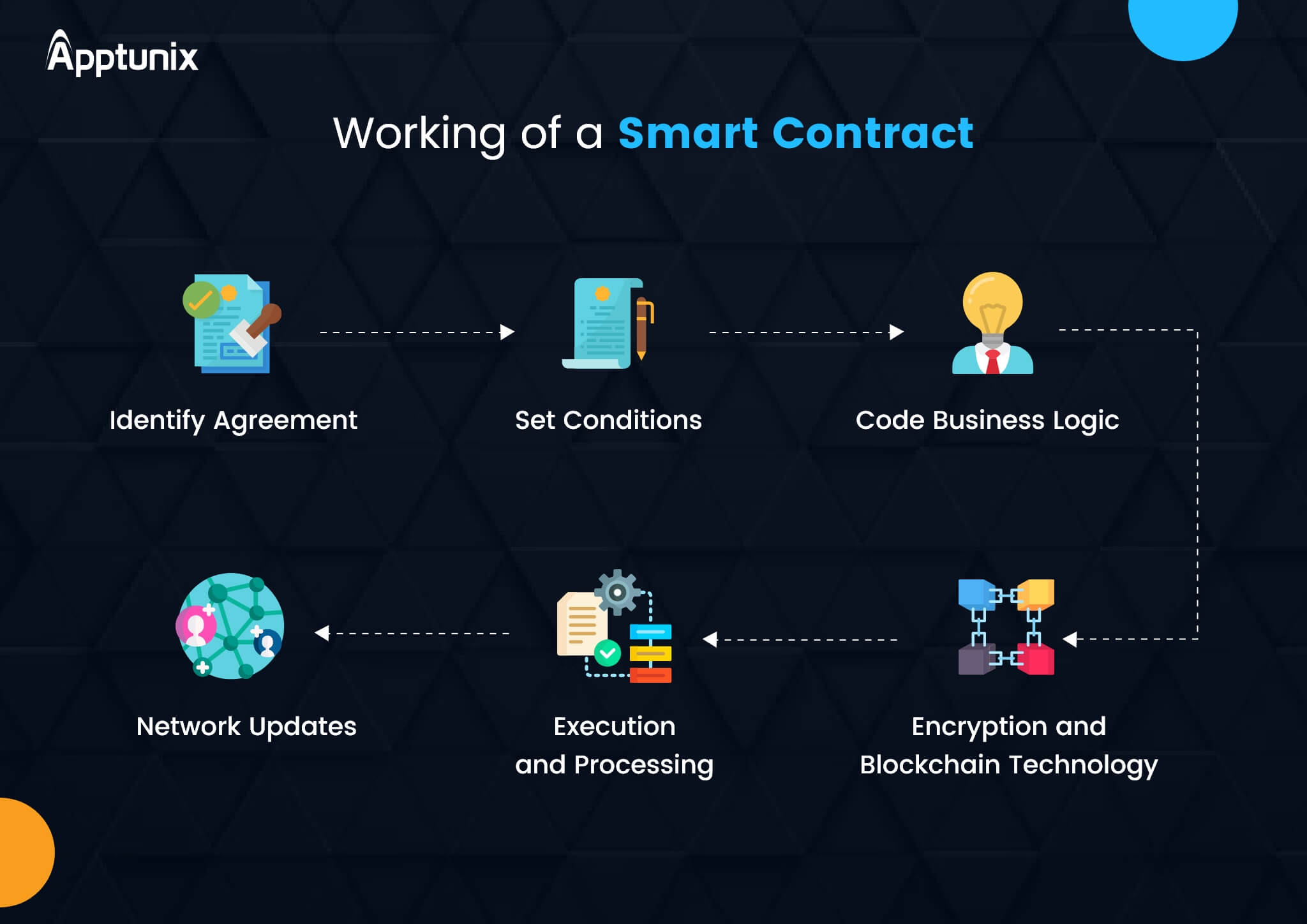
There is a lot that goes into the working of smart contracts. Let’s understand how a smart contract works with an example. Suppose, a person – say ABC – needs to sell land to another person – say XYZ – via a smart contract.
Let us assume that the transaction amount is $50,000. To accomplish the deal, the two parties will form an agreement on a blockchain platform via a smart contract that states, “If ABC receives $50,000 from XYZ, then XYZ receives the ownership of the land.”
As this smart contract is stored on the blockchain, it can’t be altered. Thus, XYZ need not worry that ABC will increase the amount demanded. Moreover, XYZ doesn’t need to pay any additional fee to a third-party like a lawyer or broker to ensure that they have made the payment.
Thus, as we can see from the above example the person doesn’t need to worry about the terms being changed or sparing extra money for closing the deal.
The terms and conditions are added to a smart contract in the form of code. Once the conditions are met, the smart contract enters execution and accomplishes what it needs to do. The final results are applied to the decentralized database of the blockchain.
What are the Business Benefits of Smart Contract Development?
There are several benefits of leveraging smart contracts development. Let’s know each one of them one by one in brief:
- Accurate – A smart contract minimizes the possibility of errors in the terms added.
- Independent – There is no involvement of any third-party as the participants of the contract are the ones who decide everything.
- Reduced Costs – In traditional contracts, parties involved in a deal need to spend additional money as commissions and fees to intermediaries. No intermediaries mean no additional expenses.
- Reliable and Secure – The smart contract is stored on a distributed network, which makes it impossible to change or counterfeit. Furthermore, the contract is stored on each node of the associated network. Hence, it can’t be lost.
- Sustainability – Unlike conventional contracts, smart contracts are digital, which means there is no requirement for paper, which makes it a more sustainable option.
Smart Contracts Development Use Cases: How Smart Contracts Can Be Used in Various Industries?
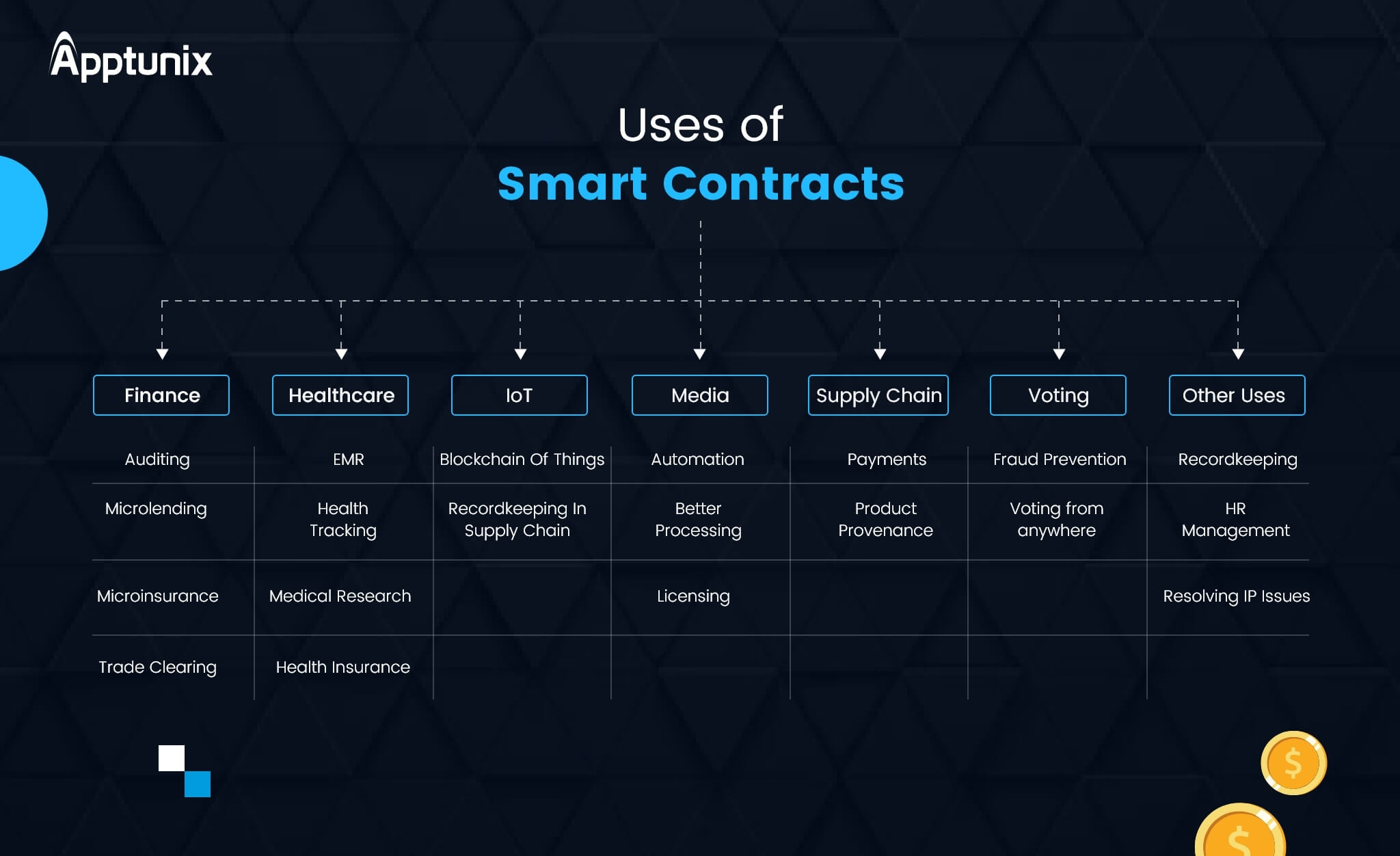
Smart contracts come useful for various purposes in different market segments. Some of the most important ones are explained below:
1. Finance
There are many walks of finance where smart contracts can be deployed. These include:
- Auditing – Facilitates stakeholders in transparent decision-making. Also, eliminates the possibility of altering accounting records by adding vital tools for bookkeeping.
- Claim Settlement – A smart contract helps to perform routing, error checking, and approval workflow. It then transfers the payment to the user upon the successful calculation of the payment to be made, which depends on the type of insurance claim and the underlying policy.
- Microinsurance – Preparing estimates and making transfers based on usage data collected from IoT devices.
- Micro-lending – Audit the value of the fundamental collateral and store the same in the database. This ensures that each transaction is fast and transparent.
- Trade Clearing – Allows managing the approval workflow between the counterparties and transferring funds upon the successful calculation of trade settlement amounts.
2. Healthcare
There are many uses for smart contracts in healthcare. These range from health insurance to health tracking and medical research. Let’s know each one of them, one at a time:
- EMR – Once the approval is made between the health service provider and the patient, a smart contract allows accessing or transferring the electronic health record.
- Health Insurance – Prevents database hacking by automatically adding patient details in policy forms. This helps to eliminate third-party intermediaries and increase efficiency.
- Health Tracking – This is another example of pairing smart contracts with IoT-enabled devices. Tracking health-based events via IoT devices.
- Medical Research – Smart contracts facilitate the collection of health data by researchers via accessing EMRs of patients who are willing to share their data for a particular fee.

3. IoT
The Internet of Things, just like blockchain, is an emerging technology that has a lot of potential. Smart contracts have a multi-faceted impact on IoT.
- BCoT – In the Blockchain of Things (BCoT), smart contracts allow IoT devices and sensors to create their own nodes in the blockchain.
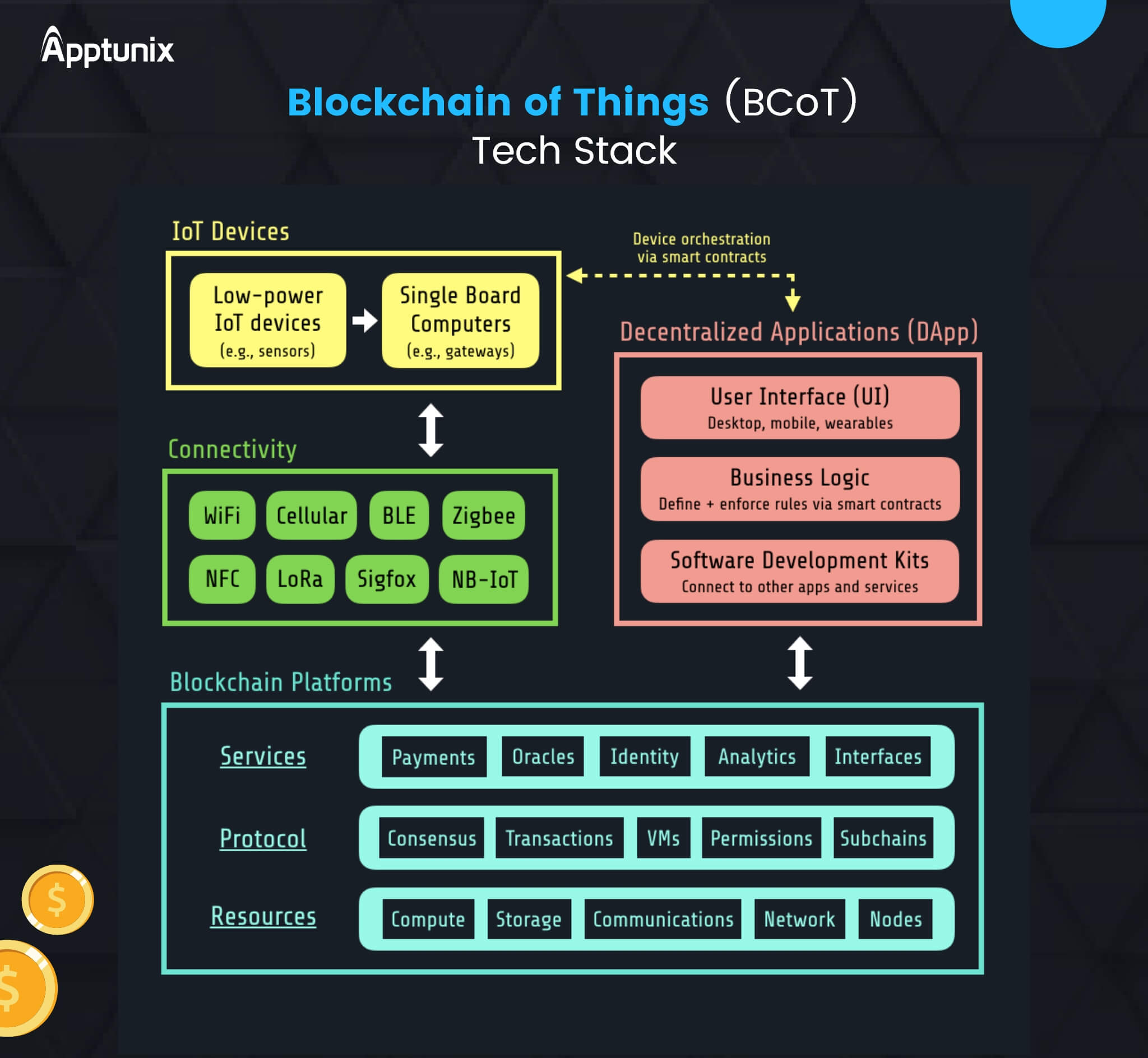
- Recordkeeping in Supply Chain – IoT devices can be used throughout the supply chain for tracking products by keeping a record of every movement. This reduces the chances of errors and theft.
4. Media
There are several benefits that smart contracts offer when it comes to selling and distributing media. This includes:
- Automation – Automation of manual transaction tasks.
- Better Processing – Accurate, cost-effective, and quicker processing.
- Licensing – The freedom to license a media in the exact way a copyright owner wants.
5. Supply Chain Management
The supply chain is a field that is immensely transformed by smart contracts, which have a galore of applications in managing supply chains, including:
- Payments – Make payments upon receiving the multi-signature approval for the letter of credit.
- Product Provenance – Issue port payments once custody change for the bills of lading is done and allow chain-of-custody for the products so that the custodian can log evidence about the same.
6. Voting
Another important use of smart contract development is for facilitating voting.
- Voting from Anywhere – Smart contracts facilitate storing public data on the blockchain. It is possible to send the information to the parties to ask them for their opinion while the data owner knows everything.
- Voter Identification – It is possible to validate voter criteria and take certain actions by entering into the blockchain system.
7. Other Uses of Smart Contracts
- Human Resource Management – Another suitable application of smart contracts is to record an employee’s academic, financial, and personal information.
- Recordkeeping – Smart contracts facilitate the storage and maintenance of records. Being secure and reliable makes them excellent for storing confidential information.
- Resolving IP Issues – Smart contracts can help to keep a track of patents and copyrights. This can help organizations save time and effort in seeking legal services for settling disputes.
How Much Does Smart Contract Development Cost?

To be frank, smart contract development isn’t cost-efficient yet. That is because the technology is still in its infancy. Hence, finding reliable service providers and experienced professionals is a challenge.
Consequently, developing a simple smart contract can cost anywhere between $7k to $15k, whereas for a complex smart contract the price can vary between $25k to $45k. Nonetheless, for a smart contract that is developed for a full-fledged organization, the price might reach or even exceed $100k.
Mind you, this cost is strictly for developing the smart contract only and not deployment (on the main net), which will further add to the overall amount that you need to spare. Other costs that you need to consider are transaction costs and audit costs.
Transactional costs are mainly influenced by network fees. Although in most cases transactions in smart contracts cost less than traditional contracts, sometimes they might be costlier. Also, the transaction fees involved depend on the Blockchain Development Platform you are using as well as the current market conditions.
Organizations offering smart contract audit services can charge anywhere between $5k to $15k. The exact amount depends on the code complexity. In certain cases, the price can be even less than $5k or greater than $15k.
What are the Limitations of Smart Contracts?
Although smart contracts development is the future, there are many pitfalls – which stem from the nature of smart contracts and the fact that they aren’t fully developed yet – that you need to avoid. So, let’s go through them one by one:
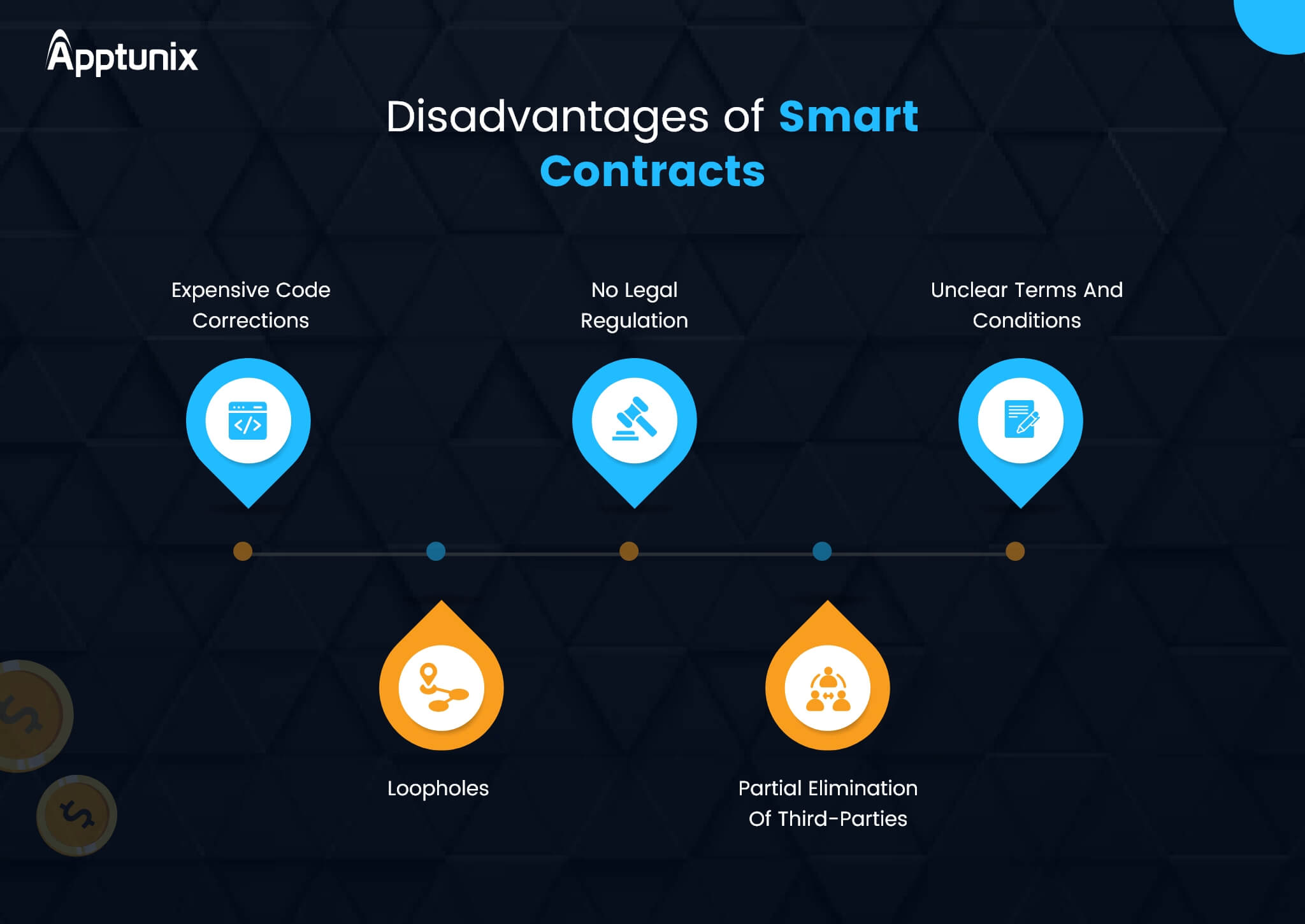
1. Immutability Means No Scope of Correction
Similar to the blockchain, smart contracts are immutable, which means once the terms are defined, they can’t be altered. This is not entirely a disadvantage – as it provides better security – but it is a double-edged sword for sure.
Even a minute error in code can cost businesses a lot of effort, time, and money to fix it. A turnaround for this is defacto mutability, where blockchain developers store segments of code in other contracts and store the location of the same in the changeable storage.
2. Incomplete Intermediary Elimination
Yes, smart contracts allow the elimination of having a third-party govern the deal, but not entirely. For now, it is not possible to eliminate third-parties completely. In fact, the roles might be changed and the third-party might be still involved, but for some other purpose and in a lesser capacity.
Let us understand this with an example. Suppose two people want to make a land-selling deal then they do not need a lawyer for developing the smart contract. However, they need to consult a lawyer to know the exact terms to be added to the smart contract.
3. Legal Involvement
In paper contracts, a dispute can be raised over an unclear statement. In smart contracts, such a case might arise if a party states that the code is buggy.
The parties involved will have to initiate a legal procedure to solve this issue, avoiding which was the primary purpose of smart contracts. Two options that can solve this problem are:
- Relying on Voting – This will only work if multiple parties are involved in the smart contract. Everyone can vote and then decide who is right.
- Introducing an Arbitrator – It can be a person or institution that will act as the judge for the dispute.
For now, it is not possible to completely remove the dependency on legal involvement until and unless the parties involved have a strong understanding of each other.
4. Loophole Exploitation
Smart contracts are yet to be regulated by the law. Thus, it is difficult to ensure that the terms met are the exact ones that were implied before executing the contract.
Many individuals and businesses are always looking forward to explicit loopholes, which is easier with something like smart contracts that don’t come under the jurisdiction of the law.
5. Unclear T&C
If you have gone through the terms and conditions of anything, one thing that you might have noticed is that almost nothing is entirely black or white. A contract has numerous terms and conditions that are implied. Hence, their meaning might differ from context to context.
It might be easy to make the terms and conditions of a smart contract simple if only a few parties are involved. However, doing the same when a huge number of parties are involved becomes almost next to impossible.
Conclusion
So you see, smart contracts development is on the rise. Also, there are several sectors that can use the concept for making life easier for both businesses and consumers.
The concept of smart contracts is still in its infancy. Therefore, there are many limitations that you need to consider before delving into smart contract development. Thankfully, with careful planning and thoughtful partnerships, these can be mitigated.
You may expect major developments in the field of smart contracts in the near future. With the rise of blockchain-powered tech, we are yet to see smart contracts in full-fledged action.
If you aren’t sure whether you should go for smart contract development, you can contact Apptunix. Our experts will analyze your requirements and objectives, and then offer you sound advice.

Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q 1.What is smart contract development?
Smart contract development is the process of developing a smart contract and deploying it onto a blockchain platform.
Q 2.How to develop smart contracts?
At our blockchain development company, we specialize in smart contract development. Explore top platforms like Avalanche, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Solana for your project needs
Q 3.What are the limitations of smart contracts?
Smart contracts aren’t fully developed yet. As such, smart contracts face issues like legal uncertainty, incomplete elimination of third-parties, and the need to add legal services for conflict resolution.
Q 4.What are some of the most popular blockchain platforms for smart contracts?
Avalanche, Algorand, Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and Solana are five of the most popular blockchain platforms for deploying smart contracts.
Rate this article!
Join 60,000+ Subscribers
Get the weekly updates on the newest brand stories, business models and technology right in your inbox.
Akhil has been writing content since 2014. Although he has written content across various niches, his forte is technology writing. Throughout his tenure he has worked in various capacities. He is presently working as the Marketing Manager for Apptunix.

App Monetization Strategies: How to Make Money From an App?
Your app can draw revenue in many ways. All you need to figure out is suitable strategies that best fit your content, your audience, and your needs. This eGuide will put light on the same.
Download Now!Subscribe to Unlock
Exclusive Business
Insights!
And we will send you a FREE eBook on Mastering Business Intelligence.